[ Home ] [ Controlled Substances ] [ Depressants ]
PINAZEPAM
|
Pinazepam, a benzodiazepine derivative, differs from other drugs of its class by the presence of an unsaturated bond, the propargyl group, at the N-1 position. In animals, pinazepam controls anxiety and aggressiveness and exerts anticonvulsant activity. In clinical trials with open or controlled design, pinazepam, compared with diazepam, showed significant and purely anxiolytic action in patients suffering from anxiety with or without somatic manifestations, particularly in gastrointestinal disorders. Even though it is not a specific hypnotic drug, it seems to help patients in whom the physiological course of the sleep is disturbed. Pinazepam is used in the treatment of anxiety and insomnia associated with anxiety.
 Pinazepam:
Pinazepam:
https://drugs.ncats.io/drug/5286RBZ882
Action:
Description: Pinazepam is a long-acting benzodiazepine with general properties similar to diazepam.
Adverse Reactions:
Drowsiness, sedation, muscle weakness and ataxia; less frequently vertigo, headache, confusion, depression, slurred speech, changes in libido, tremor, visual disturbances, urinary retention, GI disturbances, changes in salivation and amnesia; rarely, jaundice, blood disorders and hypersensitivity reactions; pain and thrombophloebitis; raised liver enzyme values; paradoxical excitation.
Drug Interactions:
Enhanced sedation or resp and CV depression with drugs with CNS depressant properties e.g. alcohol, antidepressants, antihistamines, antipsychotics, general anaesthetics, other hypnotics or sedatives, opioid analgesics and cisapride.

https://www.mims.com/singapore/drug/info/pinazepam?mtype=generic
Pinazepam is used for Anxiety, Aggressiveness and other conditions.
Is Pinazepam safe to use when pregnant?
Yes
Is Pinazepam safe while breastfeeding?
Yes
Is it safe to drive or operate heavy machinery?
If you experience drowsiness, dizziness, hypotension or a headache as side-effects when using Pinazepam medicine then it may not be safe to drive a vehicle or operate heavy machinery. One should not drive a vehicle if using the medicine makes you drowsy, dizzy or lowers your blood-pressure extensively. Pharmacists also advise patients not to drink alcohol with medicines as alcohol intensifies drowsiness side-effects. Please check for these effects on your body when using Pinazepam. Always consult with your doctor for recommendations specific to your body and health conditions.
High Risk Groups:
Should not be given to:
- Cardiac / Hypertensive Patients
- Patients suffering from Kidney dysfunction
- Patients suffering from Liver Malfunction
- Pregnant Mothers
Perform periodic blood counts and liver function tests during long term therapy. Pinazepam should be used with caution in patients if increased salivation cause respiratory difficulty, because it may produce an increase in salivation. Give least amount of drug to patients in whom depression accompanies anxiety and suicidal tendencies may be present. It should be used with caution (if it contain tartrazine) in patients with aspirin hypersensitivity because it may cause allergic reaction (including bronchial asthma).

http://www.druginfosys.com/drug.aspx?drugCode=965&type=1
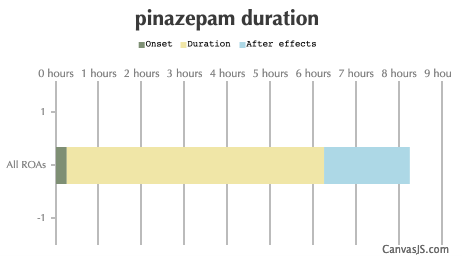
| Duration: Benzodiazepine that is solely an anxiolytic drug that lacks the hypnotic and motor impairment that most benzodiazepines do. The main metabolite of this is Nordazepam and to a lesser effect Oxazepam, which is where it gets most of its effects. | |||
| Route | Onset | Duration | After Effects |
|---|---|---|---|
| Tripsit Factsheets | |||

Pinazepam Basic Information: http://drugs.tripsit.me/pinazepam | |||
| All ROAs: | 15-90 minutes | 6-16 hours | 2-10 hours |
| |||
| Avoid: All CNS depressants. | |||
| Chemical Safety Summary: |
|---|
| INCHEM |
| Main risks and target organs: |
| Central nervous system, causing depression of respiration and consciousness. |
| Summary of clinical effects: |
| Central nervous system (CNS) depression and coma, or paradoxical excitation, but deaths are rare when benzodiazepines are taken alone. Deep coma and other manifestations of severe CNS depression are rare. Sedation, somnolence, diplopia, dysarthria, ataxia and intellectual impairment are the most common adverse effects of benzodiazepines. Overdose in adults frequently involves co- ingestion of other CNS depressants, which act synergistically to increase toxicity. Elderly and very young children are more susceptible to the CNS depressant action. Intravenous administration of even therapeutic doses of benzodiazepines may produce apnoea and hypotension. Dependence may develop with regular use of benzodiazepines, even in therapeutic doses for short periods. If benzodiazepines are discontinued abruptly after regular use, withdrawal symptoms may develop. The amnesia produced by benzodiazepines can have medico-legal consequences. |
A benzodiazepine:
- Pinazepam (marketed under the brand name Pinazepam and Duna) is a drug which is a benzodiazepine.
- Pinazepam is a moderately basic compound (based on its pKa).
- Pinazepam is a potentially toxic compound.
- Belongs to the class of organic compounds known as 1,4-benzodiazepines
Flumazenil (Anexate) is a competitive benzodiazepine receptor antagonist that can be used as an antidote for benzodiazepine overdose.
 Metabocard for Pinazepam:
Metabocard for Pinazepam:
https://hmdb.ca/metabolites/HMDB0041988
- A benzodiazepine drug
- It possesses anxiolytic, anticonvulsant, sedative and skeletal muscle relaxant properties.
- It is less toxic than diazepam
- Pinazepam is rapidly absorbed after oral administration.
Pinazepam acts as a pure anxiolytic agent - it does not possess the other pharmacological characteristics of benzodiazepines.
Its lack of intellectual, motor and hypnotic impairing effects makes it more appropriate than other benzodiazepines for day time use.
- The elimination half-life is longer in the elderly.

| Depressants | Link to this page |